npm install -g demo-joplin
To start it, type demo-joplin.
Usage
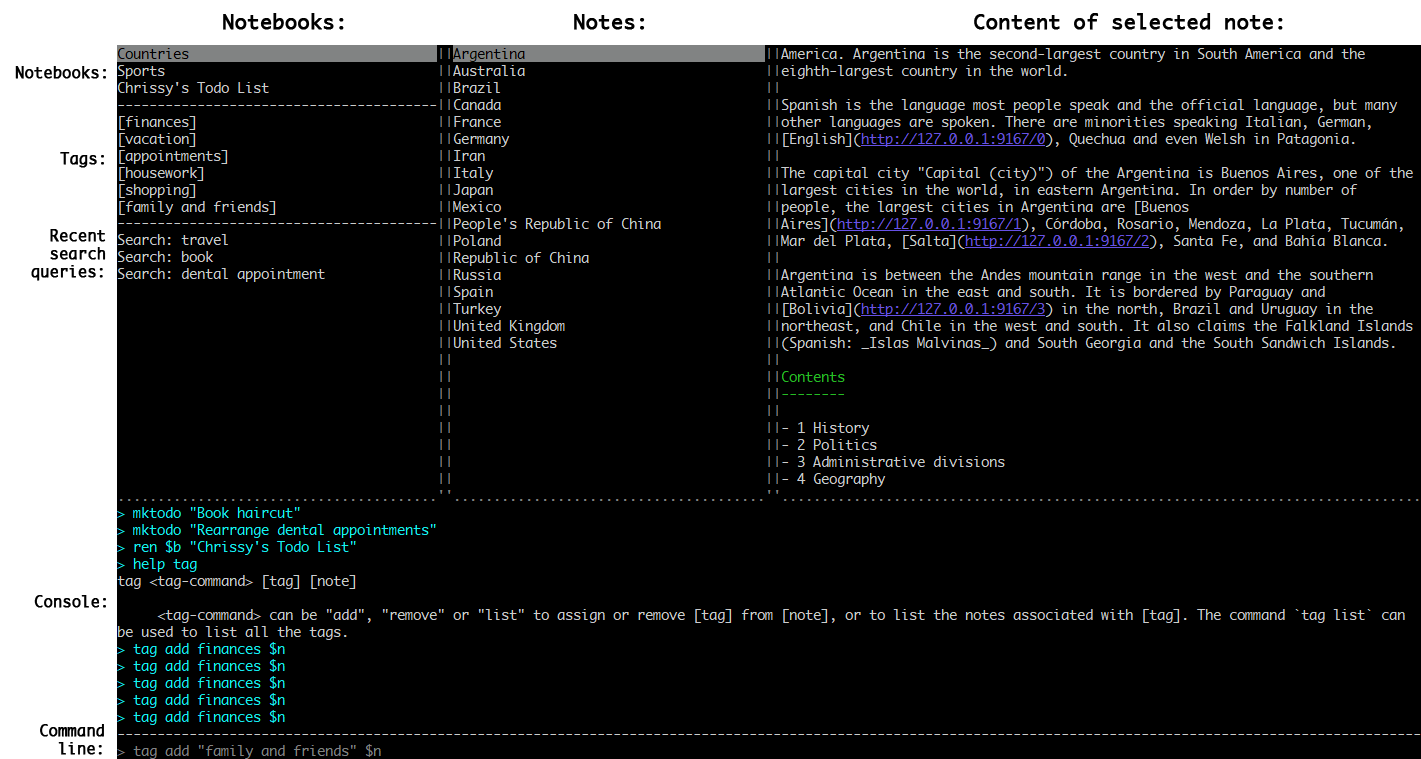
-To start the application type joplin. This will open the user interface, which has three main panes: Notebooks, Notes and the text of the current note. There are also additional panels that can be toggled on and off via shortcuts.
To start the application type joplin. This will open the user interface, which has three main panes: Notebooks, Notes and the text of the current note. There are also additional panels that can be toggled on and off via shortcuts.
Input modes
Joplin user interface is partly based on the text editor Vim and offers two different modes to interact with the notes and notebooks:
Normal mode
-Allows moving from one pane to another using the Tab and Shift-Tab keys, and to select/view notes using the arrow keys. Text area can be scrolled using the arrow keys too. Press Enter to edit a note. Various other shortcuts are available.
Allows moving from one pane to another using the Tab and Shift-Tab keys, and to select/view notes using the arrow keys. Text area can be scrolled using the arrow keys too. Press Enter to edit a note. Various other shortcuts are available.
Command-line mode
-Press : to enter command line mode. From there, the Joplin commands such as mknote or search are available. See the full list of commands.
Press : to enter command line mode. From there, the Joplin commands such as mknote or search are available. See the full list of commands.
It is possible to refer to a note or notebook by title or ID. However the simplest way is to refer to the currently selected item using one of these shortcuts:
type |
-The command type. It can have the value "exec", "function" or "prompt". exec: Simply execute the provided command. For example edit $n would edit the selected note. function: Run a special commands (see below for the list of function. prompt: A bit similar to "exec", except that the command is not going to be executed immediately - this allows the user to provide additional data. For example mknote "" would fill the command line with this command and allow the user to set the title. A prompt command can also take a cursorPosition parameter (see below) |
+The command type. It can have the value "exec", "function" or "prompt". exec: Simply execute the provided command. For example edit $n would edit the selected note. function: Run a special commands (see below for the list of functions). prompt: A bit similar to "exec", except that the command is not going to be executed immediately - this allows the user to provide additional data. For example mknote "" would fill the command line with this command and allow the user to set the title. A prompt command can also take a cursorPosition parameter (see below) |
command |
@@ -375,11 +397,11 @@ dn mv $n ""
||
cusorPosition |
-An integer. For prompt commands, tells where the cursor (caret) should start at. This is convenient for example to position the cursor between quotes. Use a negative value to set a position starting from the end. | +An integer. For prompt commands, tells where the cursor (caret) should start at. This is convenient for example to position the cursor between quotes. Use a negative value to set a position starting from the end. A value of "0" means positioning the caret at the first character. A value of "-1" means positioning it at the end. |
This is the list of available functions:
+This is the list of special functions:
As an example, this is the default keymap:
-[
- { "keys": [":"], "type": "function", "command": "enter_command_line_mode" },
- { "keys": ["TAB"], "type": "function", "command": "focus_next" },
- { "keys": ["SHIFT_TAB"], "type": "function", "command": "focus_previous" },
- { "keys": ["UP"], "type": "function", "command": "move_up" },
- { "keys": ["DOWN"], "type": "function", "command": "move_down" },
- { "keys": ["PAGE_UP"], "type": "function", "command": "page_up" },
- { "keys": ["PAGE_DOWN"], "type": "function", "command": "page_down" },
- { "keys": ["ENTER"], "type": "function", "command": "activate" },
- { "keys": ["DELETE", "BACKSPACE"], "type": "function", "command": "delete" },
- { "keys": [" "], "command": "todo toggle $n" },
- { "keys": ["tc"], "type": "function", "command": "toggle_console" },
- { "keys": ["tm"], "type": "function", "command": "toggle_metadata" },
- { "keys": ["/"], "type": "prompt", "command": "search \"\"", "cursorPosition": -2 },
- { "keys": ["mn"], "type": "prompt", "command": "mknote \"\"", "cursorPosition": -2 },
- { "keys": ["mt"], "type": "prompt", "command": "mktodo \"\"", "cursorPosition": -2 },
- { "keys": ["mb"], "type": "prompt", "command": "mkbook \"\"", "cursorPosition": -2 },
- { "keys": ["yn"], "type": "prompt", "command": "cp $n \"\"", "cursorPosition": -2 },
- { "keys": ["dn"], "type": "prompt", "command": "mv $n \"\"", "cursorPosition": -2 }
-]
-Available commands
+Commands
The following commands are available in command-line mode:
attach <note> <file>
Attaches the given file to the note.
+cat <note>
+
+ Displays the given note.
+
+ -v, --verbose Displays the complete information about note.
+
config [name] [value]
Gets or sets a config value. If [value] is not provided, it will show the
@@ -472,11 +478,6 @@ config [name] [value]
Possible keys/values:
- sync.2.path File system synchronisation target directory.
- The path to synchronise with when file system
- synchronisation is enabled. See `sync.target`.
- Type: string.
-
editor Text editor.
The editor that will be used to open a note. If
none is provided it will try to auto-detect the
@@ -485,8 +486,12 @@ Possible keys/values:
locale Language.
Type: Enum.
- Possible values: en_GB (English), es_CR (Español),
- fr_FR (Français).
+ Possible values: en_GB (English), de_DE (Deutsch),
+ es_CR (Español (Costa Rica)), es_ES (Español), eu
+ (Basque), fr_FR (Français), hr_HR (Croatian), it_IT
+ (Italiano), ja_JP (日本語), nl_BE (Nederlands), pt_BR
+ (Português (Brasil)), ru_RU (Русский), zh_CN (中文
+ (简体)).
Default: "en_GB"
dateFormat Date format.
@@ -517,14 +522,38 @@ Possible keys/values:
Default: 300
sync.target Synchronisation target.
- The target to synchonise to. If synchronising with
- the file system, set `sync.2.path` to specify the
- target directory.
+ The target to synchonise to. Each sync target may
+ have additional parameters which are named as
+ `sync.NUM.NAME` (all documented below).
Type: Enum.
Possible values: 2 (File system), 3 (OneDrive), 4
- (OneDrive Dev (For testing only)).
+ (OneDrive Dev (For testing only)), 5 (Nextcloud), 6
+ (WebDAV).
Default: 3
+ sync.2.path Directory to synchronise with (absolute path).
+ The path to synchronise with when file system
+ synchronisation is enabled. See `sync.target`.
+ Type: string.
+
+ sync.5.path Nexcloud WebDAV URL.
+ Type: string.
+
+ sync.5.username Nexcloud username.
+ Type: string.
+
+ sync.5.password Nexcloud password.
+ Type: string.
+
+ sync.6.path WebDAV URL.
+ Type: string.
+
+ sync.6.username WebDAV username.
+ Type: string.
+
+ sync.6.password WebDAV password.
+ Type: string.
+
cp <note> [notebook]
Duplicates the notes matching <note> to [notebook]. If no notebook is
@@ -534,13 +563,36 @@ done <note>
Marks a to-do as done.
+e2ee <command> [path]
+
+ Manages E2EE configuration. Commands are `enable`, `disable`, `decrypt`,
+ `status` and `target-status`.
+
+ -p, --password <password> Use this password as master password (For
+ security reasons, it is not recommended to use
+ this option).
+ -v, --verbose More verbose output for the `target-status`
+ command
+
edit <note>
Edit note.
-exit
+encrypt-config <command>
- Exits the application.
+ Manages encryption configuration.
+
+ -p, --password <password> Use this password as master password (For
+ security reasons, it is not recommended to use
+ this option).
+
+encryption <command>
+
+ Manages encryption configuration.
+
+ -p, --password <password> Use this password as master password (For
+ security reasons, it is not recommended to use
+ this option).
export <directory>
@@ -596,9 +648,18 @@ rmnote <note-pattern>
-f, --force Deletes the notes without asking for confirmation.
-search <pattern> [notebook]
+set <note> <name> [value]
- Searches for the given <pattern> in all the notes.
+ Sets the property <name> of the given <note> to the given [value].
+ Possible properties are:
+
+ parent_id (text), title (text), body (text), created_time (int),
+ updated_time (int), is_conflict (int), latitude (numeric), longitude
+ (numeric), altitude (numeric), author (text), source_url (text), is_todo
+ (int), todo_due (int), todo_completed (int), source (text),
+ source_application (text), application_data (text), order (int),
+ user_created_time (int), user_updated_time (int), encryption_cipher_text
+ (text), encryption_applied (int)
status
@@ -610,7 +671,6 @@ sync
--target <target> Sync to provided target (defaults to sync.target config
value)
- --random-failures For debugging purposes. Do not use.
tag <tag-command> [tag] [note]
@@ -629,6 +689,11 @@ undone <note>
Marks a to-do as non-completed.
+use <notebook>
+
+ Switches to [notebook] - all further operations will happen within this
+ notebook.
+
version
Displays version information