Joplin is a free, open source note taking and to-do application, which can handle a large number of notes organised into notebooks. The notes are searchable, can be copied, tagged and modified with your own text editor.
Notes exported from Evernote via .enex files can be imported into Joplin, including the formatted content (which is converted to markdown), resources (images, attachments, etc.) and complete metadata (geolocation, updated time, created time, etc.).
The notes can be synchronised with various targets including the file system (for example with a network directory) or with Microsoft OneDrive. When synchronising the notes, notebooks, tags and other metadata are saved to plain text files which can be easily inspected, backed up and moved around.
The application is still under development but is out of Beta and should be suitable for every day use. The UI of the terminal client is built on top of the great terminal-kit library, and the Android client front end is done using React Native.
Installation
npm install -g joplin
To start it, type joplin.
Demo
The demo application shows various Wikipedia articles converted to Markdown and organised into notebooks, as well as an example to-do list, in order to test and demonstrate the application. The demo application and its settings will be installed in a separate directory so as not to interfere with any existing Joplin application.
npm install -g demo-joplin
To start it, type demo-joplin.
Features
- Mobile and command line applications.
- Support notes, to-dos, tags and notebooks.
- Offline first, so the entire data is always available on the device.
- Ability to synchronise with multiple targets, including the file system and OneDrive (Dropbox is planned).
- Synchronises to a plain text format, which can be easily manipulated, backed up, or exported to a different format.
- Plain text notes, which are rendered as markdown in the mobile application.
- Tag support
- File attachment support (likewise, all file attachments can be imported from Evernote but currently cannot be manually added to a note)
- Search functionality.
- Geo-location support.
- Supports multiple languages.
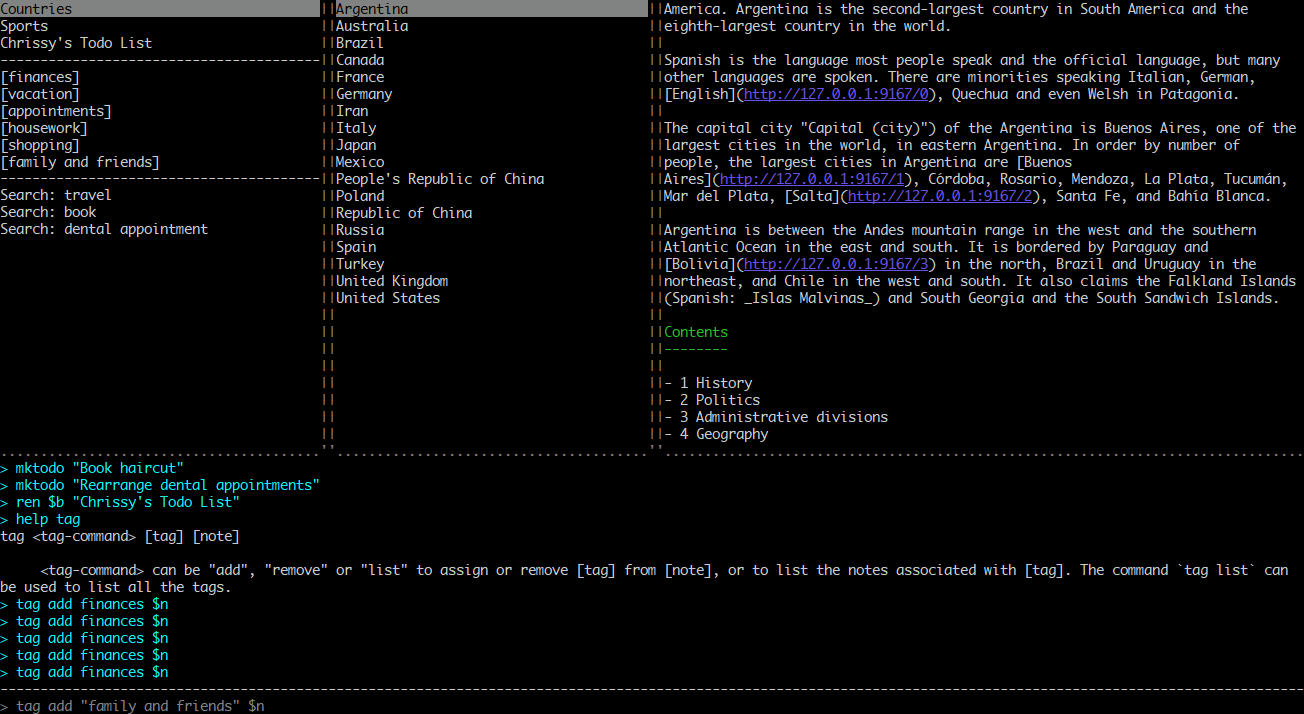
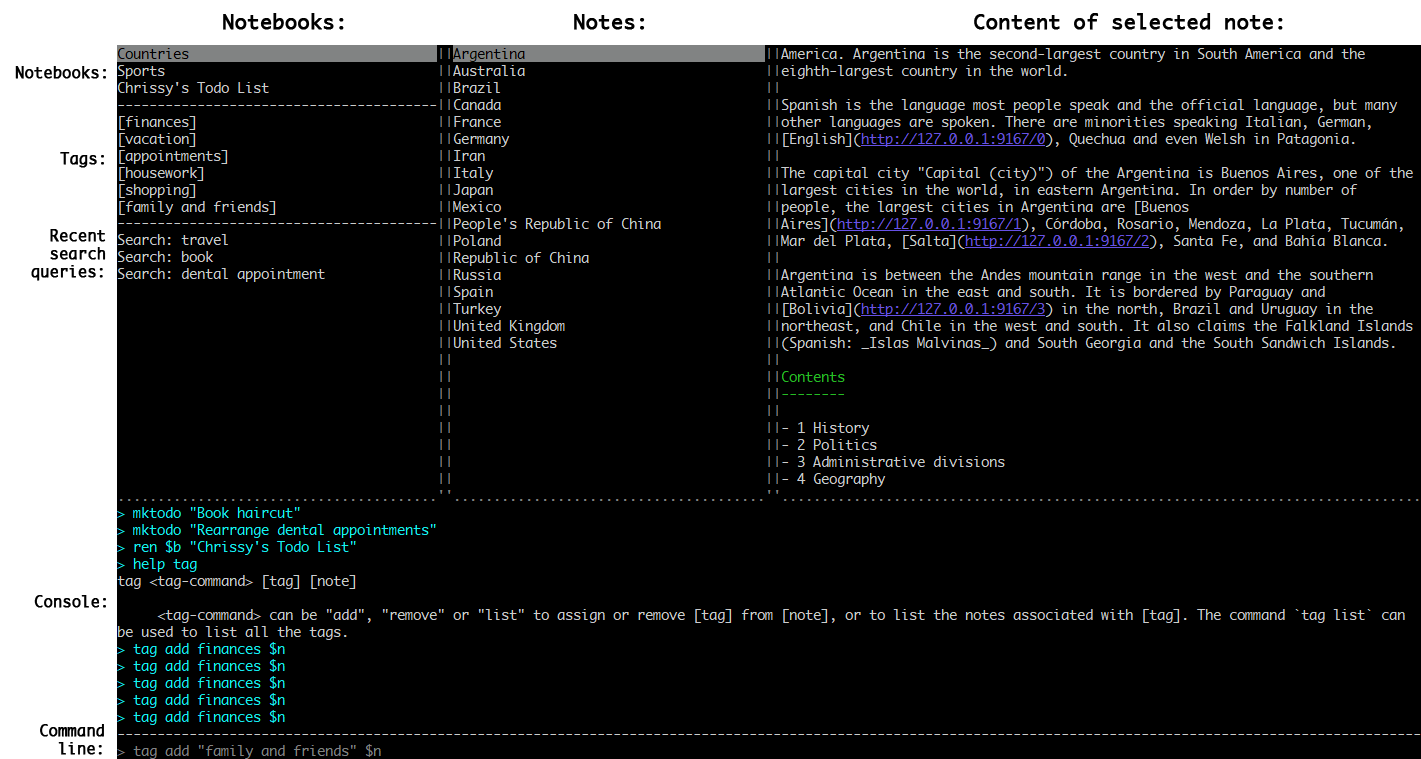
Usage
To start the application type joplin. This will open the user interface, which has three main panes: Notebooks, Notes and the text of the current note. There are also additional panels that can be toggled on and off via shortcuts.
Input modes
Joplin user interface is partly based on the text editor Vim and offers two different modes to interact with the notes and notebooks:
Normal mode
Allows moving from one pane to another using the Tab and Shift-Tab keys, and to select/view notes using the arrow keys. Text area can be scrolled using the arrow keys too. Press Enter to edit a note. Various other shortcuts are available.
Command-line mode
Press : to enter command line mode. From there, the Joplin commands such as mknote or search are available. See the full list of commands.
It is possible to refer to a note or notebook by title or ID. However the simplest way is to refer to the currently selected item using one of these shortcuts:
| Shortcut | Description |
|---|---|
$n |
Refers to the currently selected note |
$b |
Refers to the currently selected notebook |
$c |
Refers to the currently selected item. For example, if the note list is current active, $c will refer to the currently selected note. |
Examples:
Create a new note with title "Wednesday's meeting":
mknote "Wednesday's meeting"
Create a new to-do:
mktodo "Buy bread"
Move the currently selected note ($n) to the notebook with title "Personal"
mv $n "Personal"
Rename the currently selected notebook ($b) to "Something":
ren $b "Something"
Attach a local file to the currently selected note ($n):
ren $n /home/laurent/pictures/Vacation12.jpg
The configuration can also be changed from command-line mode. For example, to change the current editor to Sublime Text:
config editor "subl -w"
Getting help
The complete usage information is available from command-line mode, by typing one of these commands:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
help |
General help information |
help shortcuts |
Lists the available shortcuts |
help [command] |
Displays information about a particular command |
If the help is not fully visible, press Tab multiple times till the console is in focus and use the arrow keys or page up/down to scroll the text.
Editing a note
To edit a note, select it and press ENTER. Or, in command-line mode, type edit $n to edit the currently selected note, or edit "Note title" to edit a particular note.
Importing notes from Evernote
Joplin was designed as a replacement for Evernote and so can import complete Evernote notebooks, as well as notes, tags, resources (attached files) and note metadata (such as author, geo-location, etc.) via ENEX files. In terms of data, the only two things that might slightly differ are:
Recognition data - Evernote images, in particular scanned (or photographed) documents have recognition data associated with them. It is the text that Evernote has been able to recognise in the document. This data is not preserved when the note are imported into Joplin. However, should it become supported in the search tool or other parts of Joplin, it should be possible to regenerate this recognition data since the actual image would still be available.
Colour, font sizes and faces - Evernote text is stored as HTML and this is converted to Markdown during the import process. For notes that are mostly plain text or with basic formatting (bold, italic, bullet points, links, etc.) this is a lossless conversion, and the note, once rendered back to HTML should be very similar. Tables are also imported and converted to Markdown tables. For very complex notes, some formatting data might be loss - in particular colours, font sizes and font faces will not be imported. The text itself however is always imported in full regardless of formatting.
To import Evernote data, follow these steps:
- First, export your Evernote notebooks to ENEX files as described here.
- In Joplin, in command-line mode, type
import-enex /path/to/file.enex. This will import the notes into a new notebook named after the filename. - Then repeat the process for each notebook that needs to be imported.
Synchronisation
Joplin does synchronisation by creating simple text files that represent notes, notebooks, tags and resources. These files can then be synchronised with OneDrive or any other supported target (currently it can also synchronise with the local file system; and a Dropbox driver is also planned). When syncing, Joplin creates a sub-directory in OneDrive, in /Apps/Joplin and read/write the notes and notebooks from it. The application does not have access to anything outside this directory. To initiate the synchronisation process, type :sync. You will be asked to follow a link to authorise the application. After that, the application will synchronise in the background whenever it is running. It's possible to also synchronise outside of the user interface by typing joplin sync. This can be used to setup a cron script to synchronise at regular interval. For example, this would do it every 30 minutes:
*/30 * * * * /path/to/joplin sync
Android client
An Android client is available and can synchronise with the terminal client via OneDrive:
URLs
When Ctrl+Clicking a URL, most terminals will open that URL in the default browser. However, one issue, especially with long URLs, is that they can end up like this:
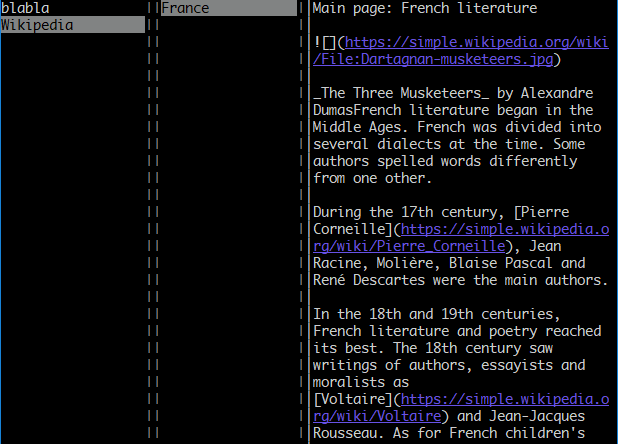
Not only it makes the text hard to read, but the link, being cut in two, will also not be clickable.
As a solution Joplin tries to start a mini-server in the background and, if successful, all the links will be converted to a much shorter URL:
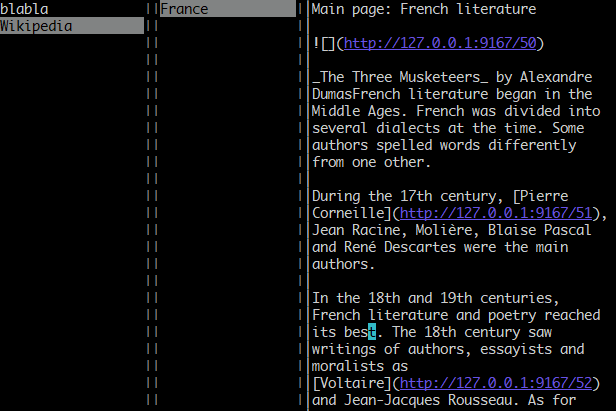
Since this is still an actual URL, the terminal will still make it clickable. And with shorter URLs, the text is more readable and the links unlikely to be cut. Both resources (files that are attached to notes) and external links are handled in this way.
Attachments / Resources
In Markdown, links to resources are represented as a simple ID to the resource. In order to give access to these resources, they will be, like links, converted to local URLs. Clicking this link will then open a browser, which will handle the file - i.e. display the image, open the PDF file, etc.
Localisation
Joplin is currently available in English and French. If you would like to contribute a translation, it is quite straightforward, please follow these steps:
- Download Poedit, the translation editor, and install it.
- Download the file to be translated.
- In Poedit, open this .pot file, go into the Catalog menu and click Configuration. Change "Country" and "Language" to your own country and language.
- From then you can translate the file. Once it's done, please send the file to this address or open a pull request.
This translation will apply to both the terminal and the Android application.
Available shortcuts
There are two types of shortcuts: those that manipulate the user interface directly, such as TAB to move from one pane to another, and those that are simply shortcuts to actual commands. In a way similar to Vim, these shortcuts are generally a verb followed by an object. For example, typing mn ([m]ake [n]ote), is used to create a new note: it will switch the interface to command line mode and pre-fill it with mknote "" from where the title of the note can be entered. See below for the full list of shortcuts:
Tab Give focus to next pane
Shift+Tab Give focus to previous pane
: Enter command line mode
ESC Exit command line mode
ENTER Edit the selected note
Ctrl+C Cancel the current command.
Ctrl+D Exit the application.
DELETE Delete the currently selected note or notebook.
SPACE Set a to-do as completed / not completed
tc [t]oggle [c]onsole between maximized/minimized/hidden/visible.
/ Search
tm [t]oggle note [m]etadata.
mn [M]ake a new [n]ote
mt [M]ake a new [t]odo
mb [M]ake a new note[b]ook
yn Copy ([Y]ank) the [n]ote to a notebook.
dn Move the note to a notebook.
Available commands
The following commands are available in command-line mode:
attach <note> <file>
Joindre le fichier fourni à la note.
config [name] [value]
Obtient ou modifie une valeur de configuration. Si la [valeur] n'est pas
fournie, la valeur de [nom] est affichée. Si ni le [nom] ni la [valeur] ne
sont fournis, la configuration complète est affichée.
-v, --verbose Afficher également les variables cachées.
Clefs/Valeurs possibles :
editor Editeur de texte.
L'éditeur de texte pour ouvrir et modifier les
notes. Si aucun n'est spécifié, il sera détecté
automatiquement.
Type : string.
locale Langue.
Type : Enum.
Valeurs possibles : en_GB (English), fr_FR
(Français).
Défaut : "en_GB"
sync.2.path Cible de la synchronisation sur le disque dur.
Le chemin du répertoire avec lequel synchroniser
lorsque la synchronisation par système de fichier
est activée. Voir `sync.target`.
Type : string.
sync.interval Interval de synchronisation.
Type : Enum.
Valeurs possibles : 0 (Désactivé), 300 (5 minutes),
600 (10 minutes), 1800 (30 minutes), 3600 (1
heure), 43200 (12 heures), 86400 (24 heures).
Défaut : 300
sync.target Cible de la synchronisation.
La cible avec laquelle synchroniser. Pour
synchroniser avec le système de fichier, veuillez
spécifier le répertoire avec `sync.2.path`.
Type : Enum.
Valeurs possibles : 1 (Memory), 2 (Système de
fichier), 3 (OneDrive).
Défaut : 3
trackLocation Enregistrer l'emplacement avec les notes.
Type : bool.
Défaut : true
uncompletedTodosOnTop Tâches non-terminées en haut des listes.
Type : bool.
Défaut : true
cp <note> [notebook]
Copie les notes correspondant à <nom> vers [carnet]. Si aucun carnet n'est
spécifié, la note est dupliquée sur place.
done <note>
Marquer la tâche comme complétée.
edit <note>
Editer la note.
exit
Quitter le logiciel.
export <directory>
Exporter les données de Joplin vers le dossier fourni. Par défaut, la base
de donnée complète sera exportée, y compris les carnets, notes, tags et
resources.
--note <note> Exporter uniquement la note spécifiée.
--notebook <notebook> Exporter uniquement le carnet spécifié.
geoloc <note>
Afficher l'URL de l'emplacement de la note.
help [command]
Affiche les informations d'utilisation.
import-enex <file> [notebook]
Importer un carnet Evernote (fichier .enex).
-f, --force Ne pas demander de confirmation.
mkbook <new-notebook>
Créer un carnet.
mknote <new-note>
Créer une note.
mktodo <new-todo>
Créer une nouvelle tâche.
mv <note> [notebook]
Déplacer les notes correspondant à <note> vers [notebook].
ren <item> <name>
Renommer l'objet <item> (note ou carnet) en <name>.
rmbook <notebook>
Supprimer le carnet.
-f, --force Supprimer le carnet sans demander la confirmation.
rmnote <note-pattern>
Supprimer les notes correspondants à <note-pattern>.
-f, --force Supprimer les notes sans demander la confirmation.
search <pattern> [notebook]
Chercher le motif <pattern> dans toutes les notes.
status
Afficher un résumé des notes et carnets.
sync
Synchroniser les notes et carnets.
--target <target> Synchroniser avec la cible donnée (par défaut, la
valeur de configuration `sync.target`).
--random-failures For debugging purposes. Do not use.
tag <tag-command> [tag] [note]
<tag-command> peut être "add", "remove" ou "list" pour assigner ou enlever
l'étiquette [tag] de la [note], our pour lister les notes associées avec
l'étiquette [tag]. La commande `tag list` peut être utilisée pour lister
les étiquettes.
todo <todo-command> <note-pattern>
Gère le status des tâches. <todo-command> peut être "toggle" ou "clear".
Utilisez "toggle" pour basculer la tâche entre le status terminé et
non-terminé (Si la cible est une note, elle sera convertie en tâche).
Utilisez "clear" pour convertir la tâche en note.
undone <note>
Marquer une tâche comme non-complétée.
version
Affiche les informations de version
Known bugs
- Non-alphabetical characters such as Chinese or Arabic might create glitches in the user interface on Windows. This is a limitation of the current Windows console.
License
Copyright (c) 2016-2017 Laurent Cozic
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
Copyright (c) 2016-2017 Laurent Cozic

