mirror of
https://github.com/jesseduffield/lazygit.git
synced 2024-12-10 11:10:18 +02:00
81 lines
5.0 KiB
Markdown
81 lines
5.0 KiB
Markdown
# Integration Tests
|
|
|
|
The pkg/integration package is for integration testing: that is, actually running a real lazygit session and having a robot pretend to be a human user and then making assertions that everything works as expected.
|
|
|
|
TL;DR: integration tests live in pkg/integration/tests. Run integration tests with:
|
|
|
|
```sh
|
|
go run cmd/integration_test/main.go tui
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
or
|
|
|
|
```sh
|
|
go run cmd/integration_test/main.go cli [--slow or --sandbox] [testname or testpath...]
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
## Writing tests
|
|
|
|
The tests live in pkg/integration/tests. Each test is listed in `pkg/integration/tests/tests_gen.go` which is an auto-generated file. You can re-generate that file by running `go generate ./...` at the root of the Lazygit repo.
|
|
|
|
Each test has two important steps: the setup step and the run step.
|
|
|
|
### Setup step
|
|
|
|
In the setup step, we prepare a repo with shell commands, for example, creating a merge conflict that will need to be resolved upon opening lazygit. This is all done via the `shell` argument.
|
|
|
|
### Run step
|
|
|
|
The run step has two arguments passed in:
|
|
|
|
1. `t` (the test driver)
|
|
2. `keys`
|
|
|
|
`t` is for driving the gui by pressing certain keys, selecting list items, etc.
|
|
`keys` is for use when getting the test to press a particular key e.g. `t.Views().Commits().Focus().PressKey(keys.Universal.Confirm)`
|
|
|
|
### Tips
|
|
|
|
#### Handle most setup in the `shell` part of the test
|
|
|
|
Try to do as much setup work as possible in your setup step. For example, if all you're testing is that the user is able to resolve merge conflicts, create the merge conflicts in the setup step. On the other hand, if you're testing to see that lazygit can warn the user about merge conflicts after an attempted merge, it's fine to wait until the run step to actually create the conflicts. If the run step is focused on the thing you're trying to test, the test will run faster and its intent will be clearer.
|
|
|
|
#### Create helper functions for (very) frequently used test logic
|
|
|
|
If you find yourself doing something frequently in a test, consider making it a method in one of the helper arguments. For example, instead of calling `t.PressKey(keys.Universal.Confirm)` in 100 places, it's better to have a method `t.Confirm()`. This is not to say that everything should be made into a helper method: just things that are particularly common in tests.
|
|
|
|
Also, given how often we need to select a menu item or type into a prompt panel, there are some helper functions for that. See `ExpectConfirmation` for an example.
|
|
|
|
## Running tests
|
|
|
|
There are three ways to invoke a test:
|
|
|
|
1. go run cmd/integration_test/main.go cli [--slow or --sandbox] [testname or testpath...]
|
|
2. go run cmd/integration_test/main.go tui
|
|
3. go test pkg/integration/clients/*.go
|
|
|
|
The first, the test runner, is for directly running a test from the command line. If you pass no arguments, it runs all tests.
|
|
The second, the TUI, is for running tests from a terminal UI where it's easier to find a test and run it without having to copy it's name and paste it into the terminal. This is the easiest approach by far.
|
|
The third, the go-test command, intended only for use in CI, to be run along with the other `go test` tests. This runs the tests in headless mode so there's no visual output.
|
|
|
|
The name of a test is based on its path, so the name of the test at `pkg/integration/tests/commit/new_branch.go` is commit/new_branch. So to run it with our test runner you would run `go run cmd/integration_test/main.go cli commit/new_branch`.
|
|
|
|
You can pass the KEY_PRESS_DELAY env var to the test runner in order to set a delay in milliseconds between keypresses, which helps for watching a test at a realistic speed to understand what it's doing. Or you can pass the '--slow' flag which sets a pre-set 'slow' key delay. In the tui you can press 't' to run the test in slow mode.
|
|
|
|
The resultant repo will be stored in `test/integration`, so if you're not sure what went wrong you can go there and inspect the repo.
|
|
|
|
### Running tests in VSCode
|
|
|
|
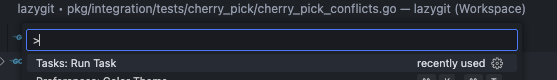
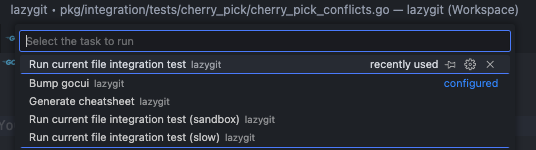
If you've opened an integration test file in your editor you can run that file by bringing up the command panel with `cmd+shift+p` and typing 'run task', then selecting the test task you want to run
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
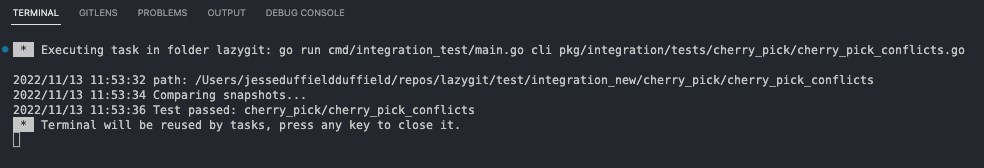
The test will run in a VSCode terminal:
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Sandbox mode
|
|
|
|
Say you want to do a manual test of how lazygit handles merge-conflicts, but you can't be bothered actually finding a way to create merge conflicts in a repo. To make your life easier, you can simply run a merge-conflicts test in sandbox mode, meaning the setup step is run for you, and then instead of the test driving the lazygit session, you're allowed to drive it yourself.
|
|
|
|
To run a test in sandbox mode you can press 's' on a test in the test TUI or in the test runner pass the --sandbox argument.
|