17 KiB
Joplin
Joplin is a free, open source note taking and to-do application, which can handle a large number of notes organised into notebooks. The notes are searchable, can be copied, tagged and modified with your own text editor.
Notes exported from Evernote via .enex files can be imported into Joplin, including the formatted content (which is converted to markdown), resources (images, attachments, etc.) and complete metadata (geolocation, updated time, created time, etc.).
The notes can be synchronised with various targets including the file system (for example with a network directory) or with Microsoft OneDrive. When synchronising the notes, notebooks, tags and other metadata are saved to plain text files which can be easily inspected, backed up and moved around.
Installation
On macOS:
brew install node joplin
On Linux or Windows (via WSL):
Important: First, install Node 8+. Node 8 is LTS but not yet available everywhere so you might need to manually install it.
NPM_CONFIG_PREFIX=~/.joplin-bin npm install -g joplin
sudo ln -s ~/.joplin-bin/bin/joplin /usr/bin/joplin
By default, the application binary will be installed under ~/.joplin-bin. You may change this directory if needed. Alternatively, if your npm permissions are setup as described here (Option 2) then simply running npm -g install joplin would work.
To start it, type joplin.
Demo
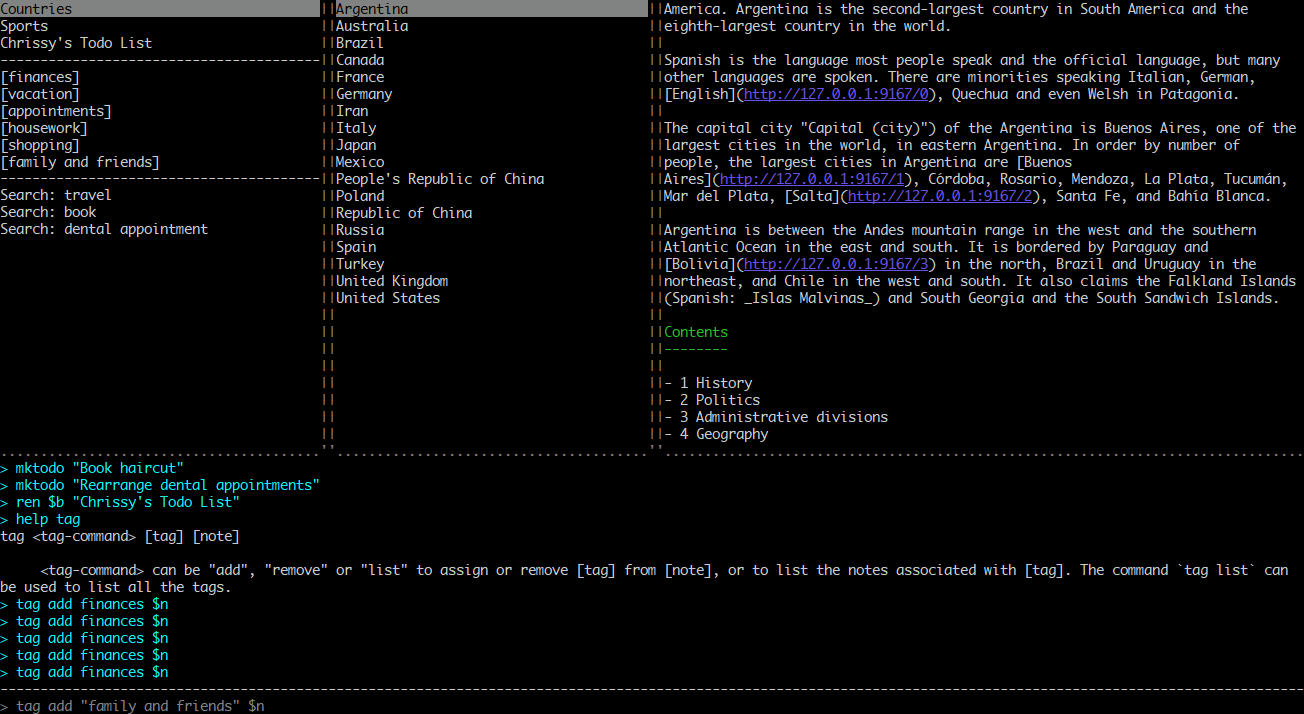
The demo application shows various Wikipedia articles converted to Markdown and organised into notebooks, as well as an example to-do list, in order to test and demonstrate the application. The demo application and its settings will be installed in a separate directory so as not to interfere with any existing Joplin application.
npm install -g demo-joplin
To start it, type demo-joplin.
Usage
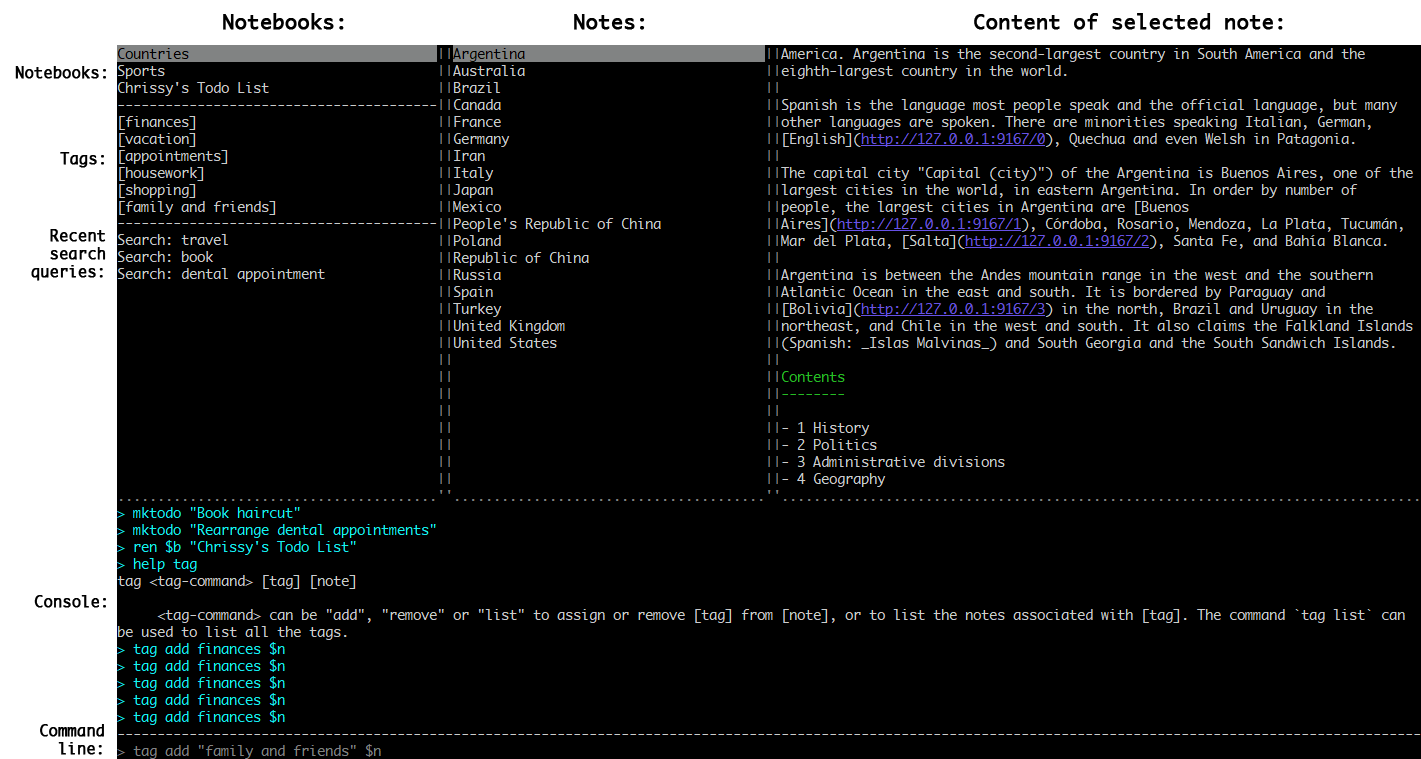
To start the application type joplin. This will open the user interface, which has three main panes: Notebooks, Notes and the text of the current note. There are also additional panels that can be toggled on and off via shortcuts.
Input modes
Joplin user interface is partly based on the text editor Vim and offers two different modes to interact with the notes and notebooks:
Normal mode
Allows moving from one pane to another using the Tab and Shift-Tab keys, and to select/view notes using the arrow keys. Text area can be scrolled using the arrow keys too. Press Enter to edit a note. Various other shortcuts are available.
Command-line mode
Press : to enter command line mode. From there, the Joplin commands such as mknote or search are available. See the full list of commands.
It is possible to refer to a note or notebook by title or ID. However the simplest way is to refer to the currently selected item using one of these shortcuts:
| Shortcut | Description |
|---|---|
$n |
Refers to the currently selected note |
$b |
Refers to the currently selected notebook |
$c |
Refers to the currently selected item. For example, if the note list is current active, $c will refer to the currently selected note. |
Examples:
Create a new note with title "Wednesday's meeting":
mknote "Wednesday's meeting"
Create a new to-do:
mktodo "Buy bread"
Move the currently selected note ($n) to the notebook with title "Personal"
mv $n "Personal"
Rename the currently selected notebook ($b) to "Something":
ren $b "Something"
Attach a local file to the currently selected note ($n):
ren $n /home/laurent/pictures/Vacation12.jpg
The configuration can also be changed from command-line mode. For example, to change the current editor to Sublime Text:
config editor "subl -w"
Editing a note
To edit a note, select it and press ENTER. Or, in command-line mode, type edit $n to edit the currently selected note, or edit "Note title" to edit a particular note.
Getting help
The complete usage information is available from command-line mode, by typing one of these commands:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
help |
General help information |
help shortcuts |
Lists the available shortcuts |
help [command] |
Displays information about a particular command |
If the help is not fully visible, press Tab multiple times till the console is in focus and use the arrow keys or page up/down to scroll the text.
Importing notes from Evernote
To import Evernote data, follow these steps:
- First, export your Evernote notebooks to ENEX files as described here.
- In Joplin, in command-line mode, type
import-enex /path/to/file.enex. This will import the notes into a new notebook named after the filename. - Then repeat the process for each notebook that needs to be imported.
Synchronisation
One of the goals of Joplin was to avoid being tied to any particular company or service, whether it is Evernote, Google or Microsoft. As such the synchronisation is designed without any hard dependency to any particular service. Most of the synchronisation process is done at an abstract level and access to external services, such as OneDrive or Dropbox, is done via lightweight drivers. It is easy to support new services by creating simple drivers that provide a filesystem-like interface, i.e. the ability to read, write, delete and list items. It is also simple to switch from one service to another or to even sync to multiple services at once. Each note, notebook, tags, as well as the relation between items is transmitted as plain text files during synchronisation, which means the data can also be moved to a different application, can be easily backed up, inspected, etc.
Currently, synchronisation is possible with OneDrive (by default) or the local filesystem. A Dropbox driver will also be available once this React Native bug is fixed. When syncing with OneDrive, Joplin creates a sub-directory in OneDrive, in /Apps/Joplin and read/write the notes and notebooks from it. The application does not have access to anything outside this directory.
To initiate the synchronisation process, type :sync. You will be asked to follow a link to authorise the application (simply input your Microsoft credentials - you do not need to register with OneDrive). After that, the application will synchronise in the background whenever it is running. It is possible to also synchronise outside of the user interface by typing joplin sync from the terminal. This can be used to setup a cron script to synchronise at regular interval. For example, this would do it every 30 minutes:
*/30 * * * * /path/to/joplin sync
URLs
When Ctrl+Clicking a URL, most terminals will open that URL in the default browser. However, one issue, especially with long URLs, is that they can end up like this:
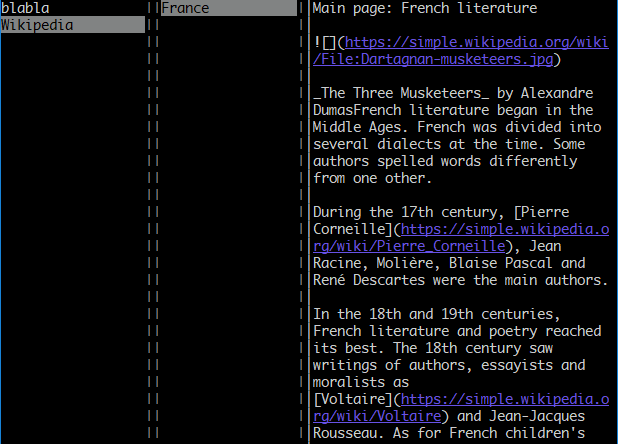
Not only it makes the text hard to read, but the link, being cut in two, will also not be clickable.
As a solution Joplin tries to start a mini-server in the background and, if successful, all the links will be converted to a much shorter URL:
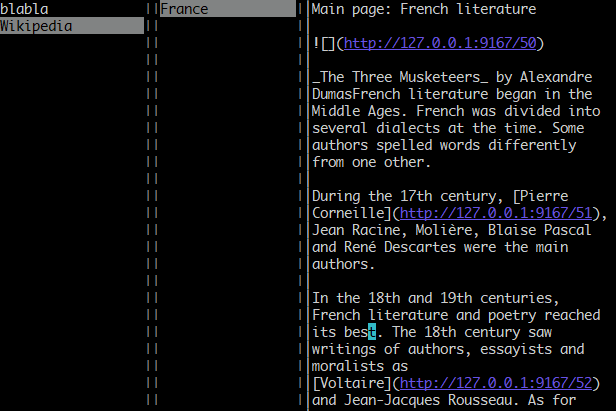
Since this is still an actual URL, the terminal will still make it clickable. And with shorter URLs, the text is more readable and the links unlikely to be cut. Both resources (files that are attached to notes) and external links are handled in this way.
Attachments / Resources
In Markdown, links to resources are represented as a simple ID to the resource. In order to give access to these resources, they will be, like links, converted to local URLs. Clicking this link will then open a browser, which will handle the file - i.e. display the image, open the PDF file, etc.
Shell mode
Commands can also be used directly from a shell. To view the list of available commands, type joplin help all. To reference a note, notebook or tag you can either use the ID (type joplin ls -l to view the ID) or by title.
For example, this will create a new note "My note" in the notebook "My notebook":
$ joplin mkbook "My notebook"
$ joplin use "My notebook"
$ joplin mknote "My note"
To view the newly created note:
$ joplin ls -l
fe889 07/12/2017 17:57 My note
Give a new title to the note:
$ joplin set fe889 title "New title"
Available shortcuts
There are two types of shortcuts: those that manipulate the user interface directly, such as TAB to move from one pane to another, and those that are simply shortcuts to actual commands. In a way similar to Vim, these shortcuts are generally a verb followed by an object. For example, typing mn ([m]ake [n]ote), is used to create a new note: it will switch the interface to command line mode and pre-fill it with mknote "" from where the title of the note can be entered. See below for the full list of shortcuts:
Tab Give focus to next pane
Shift+Tab Give focus to previous pane
: Enter command line mode
ESC Exit command line mode
ENTER Edit the selected note
Ctrl+C Cancel the current command.
Ctrl+D Exit the application.
DELETE Delete the currently selected note or notebook.
SPACE Set a to-do as completed / not completed
tc [t]oggle [c]onsole between maximized/minimized/hidden/visible.
/ Search
tm [t]oggle note [m]etadata.
mn [M]ake a new [n]ote
mt [M]ake a new [t]odo
mb [M]ake a new note[b]ook
yn Copy ([Y]ank) the [n]ote to a notebook.
dn Move the note to a notebook.
Available commands
The following commands are available in command-line mode:
attach <note> <file>
Attaches the given file to the note.
config [name] [value]
Gets or sets a config value. If [value] is not provided, it will show the
value of [name]. If neither [name] nor [value] is provided, it will list
the current configuration.
-v, --verbose Also displays unset and hidden config variables.
Possible keys/values:
sync.2.path File system synchronisation target directory.
The path to synchronise with when file system
synchronisation is enabled. See `sync.target`.
Type: string.
editor Text editor.
The editor that will be used to open a note. If
none is provided it will try to auto-detect the
default editor.
Type: string.
locale Language.
Type: Enum.
Possible values: en_GB (English), es_CR (Español),
fr_FR (Français).
Default: "en_GB"
dateFormat Date format.
Type: Enum.
Possible values: DD/MM/YYYY (30/01/2017), DD/MM/YY
(30/01/17), MM/DD/YYYY (01/30/2017), MM/DD/YY
(01/30/17), YYYY-MM-DD (2017-01-30).
Default: "DD/MM/YYYY"
timeFormat Time format.
Type: Enum.
Possible values: HH:mm (20:30), h:mm A (8:30 PM).
Default: "HH:mm"
uncompletedTodosOnTop Show uncompleted todos on top of the lists.
Type: bool.
Default: true
trackLocation Save geo-location with notes.
Type: bool.
Default: true
sync.interval Synchronisation interval.
Type: Enum.
Possible values: 0 (Disabled), 300 (5 minutes), 600
(10 minutes), 1800 (30 minutes), 3600 (1 hour),
43200 (12 hours), 86400 (24 hours).
Default: 300
sync.target Synchronisation target.
The target to synchonise to. If synchronising with
the file system, set `sync.2.path` to specify the
target directory.
Type: Enum.
Possible values: 2 (File system), 3 (OneDrive), 4
(OneDrive Dev (For testing only)).
Default: 3
cp <note> [notebook]
Duplicates the notes matching <note> to [notebook]. If no notebook is
specified the note is duplicated in the current notebook.
done <note>
Marks a to-do as done.
edit <note>
Edit note.
exit
Exits the application.
export <directory>
Exports Joplin data to the given directory. By default, it will export the
complete database including notebooks, notes, tags and resources.
--note <note> Exports only the given note.
--notebook <notebook> Exports only the given notebook.
geoloc <note>
Displays a geolocation URL for the note.
help [command]
Displays usage information.
import-enex <file> [notebook]
Imports an Evernote notebook file (.enex file).
-f, --force Do not ask for confirmation.
mkbook <new-notebook>
Creates a new notebook.
mknote <new-note>
Creates a new note.
mktodo <new-todo>
Creates a new to-do.
mv <note> [notebook]
Moves the notes matching <note> to [notebook].
ren <item> <name>
Renames the given <item> (note or notebook) to <name>.
rmbook <notebook>
Deletes the given notebook.
-f, --force Deletes the notebook without asking for confirmation.
rmnote <note-pattern>
Deletes the notes matching <note-pattern>.
-f, --force Deletes the notes without asking for confirmation.
search <pattern> [notebook]
Searches for the given <pattern> in all the notes.
status
Displays summary about the notes and notebooks.
sync
Synchronises with remote storage.
--target <target> Sync to provided target (defaults to sync.target config
value)
--random-failures For debugging purposes. Do not use.
tag <tag-command> [tag] [note]
<tag-command> can be "add", "remove" or "list" to assign or remove [tag]
from [note], or to list the notes associated with [tag]. The command `tag
list` can be used to list all the tags.
todo <todo-command> <note-pattern>
<todo-command> can either be "toggle" or "clear". Use "toggle" to toggle
the given to-do between completed and uncompleted state (If the target is
a regular note it will be converted to a to-do). Use "clear" to convert
the to-do back to a regular note.
undone <note>
Marks a to-do as non-completed.
version
Displays version information
License
Copyright (c) 2016-2017 Laurent Cozic
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.